Table of Contents
Server-Based Computing (SBC) changes the way companies handle their IT systems. Instead of managing software and data on each individual computer, SBC stores everything on one main server. This makes it easier to keep track of updates, ensure security, and save money. With SBC, employees can access what they need from any device, and the server does most of the work. In this article, we’ll look at the benefits of SBC, how it works, and some challenges to be aware of.
What is Server Based Computing?
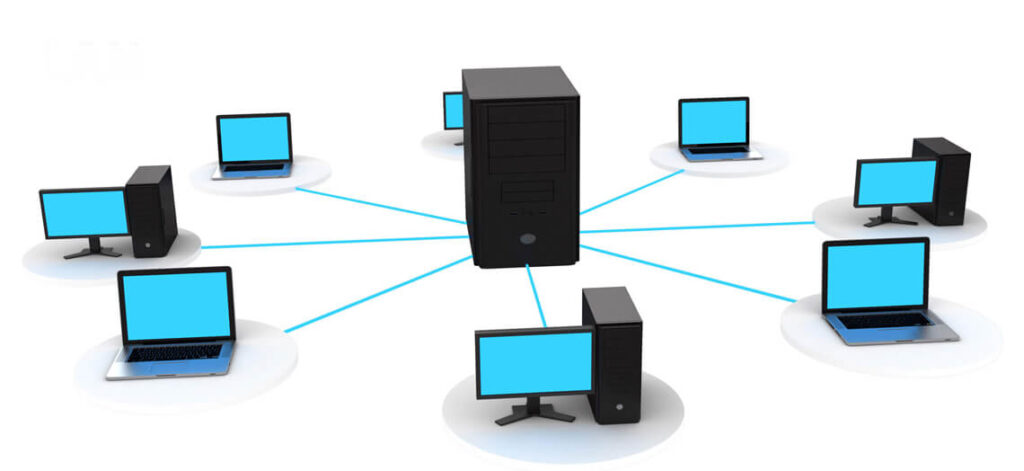
Server-Based Computing (SBC) is a technology that centralizes the management of data and applications on a server rather than on individual user devices. This model allows users to access applications and data from a central server, making it easier to manage, update, and secure resources. The core idea is to shift the processing load from end-user devices to the server, leading to a more streamlined and efficient IT infrastructure.
The Key to Efficient IT Management
Server Based Computing (SBC) is the key to managing IT more efficiently. It puts all data and applications on one central server instead of on each computer. This makes it easier to keep everything updated and secure. With SBC, you save money on hardware and IT support because you don’t need as many high-spec computers. It also makes it simpler to add new users or resources as your business grows, ensuring everyone has the latest tools and information they need.
Benefits of Server-Based Computing
1. Centralized Management
One of the primary advantages of SBC is centralized management. IT administrators can deploy, update, and manage applications and data from a single server. This reduces the complexity associated with managing multiple devices individually and ensures that all users have access to the latest software versions and updates.
2. Enhanced Security
SBC enhances security by keeping sensitive data and applications on a central server rather than on individual devices. This centralization makes it easier to implement robust security measures, such as firewalls and encryption, and to monitor and manage access controls. In case of a device failure or theft, data remains secure on the server.
3. Cost Efficiency
By centralizing resources, SBC can lead to significant cost savings. Organizations can reduce the need for high-specification hardware on individual workstations, as the server handles most of the processing. Additionally, IT support and maintenance costs are often lower, as there are fewer individual devices to manage.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
SBC provides flexibility in how users access applications and data. Users can connect to the server from various devices, including low-spec devices or even mobile phones, as long as they have an internet connection. This flexibility supports remote work and can easily scale to accommodate a growing number of users or applications.
How SBC Works?
In a typical SBC setup, users connect to a central server through a network, often using thin client devices or virtual desktops. The server handles the processing and stores the applications and data. When a user requests a file or application, the server processes the request and sends the necessary information back to the user’s device. This model ensures that the server remains the focal point of data management and application delivery.
Challenges of Server-Based Computing
While Server-Based Computing offers many benefits, it is not without its challenges. High server performance and reliability are crucial, as any downtime or failure can impact all users. Additionally, setting up and maintaining a server-based environment requires skilled IT personnel and robust network infrastructure.
Conclusion
Server-Based Computing represents a significant shift in how IT resources are managed and delivered. By centralizing data and applications on a server, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, security, and cost savings. As technology continues to evolve, SBC is likely to play an increasingly important role in IT infrastructure, providing a solid foundation for managing modern business needs.